
Technical SEO has changed over the past 20 years.
Today, content marketers focus on creating readable, flexible and smart content that readers can consume. This kind of content ranks highest on search engines and generates the best traffic. That said, even today, digital marketers need to know technical SEO best practices so their great content creates search engine success.
Cheap Tricks Don’t Work
SEO isn’t the roast beef for Sunday dinner of digital marketing. But it is the gravy.
SEO can’t generate traffic for bad content. It can only enhance content that’s already good and draw attention to that content. In the past, marketers could brute force good traffic for bad content by optimizing for the latest algorithm.
Link farms, keyword spamming, hidden keywords … there were a number of ways to trick search engines and generate high ranking results. Those tactics are gone. Good content was always important, but it’s irreplaceable now.
If people do not read and engage with your content, you won’t rank on the search engine ranking page (SERP).
Keyword Frequency
A keyword is simply a search term you wish to rank for. And keyword frequency, also known as keyword density, is a measure of how many times that search term appears on a given page.
In the early days of SEO, we wrote articles with extremely high keyword density so search engines would rank the page. Users eventually complained that articles stuffed with keywords were hard to read. Search engines got wise and changed their algorithms. Now it’s not only useless to overuse keywords, it’s actually hurtful. You can be penalized or removed from the SERP entirely if your keywords appear too often.
There are tools you can use to calculate the keyword density on your page or your site. You can also use this formula to figure it out:
([times you used keyword] / [words on page]) = density
This equation will give you a decimal — this is your keyword density. Multiple that number by 100 to get a percentage.
Google won’t release a solid percentage to shoot for; they recommend adding keywords only as they naturally match the article. SEO authorities recommend staying under 5% at the very maximum, and if possible under 2%. The ideal percentage is about 1% to keep from incurring penalties, at least for exact matches. There are other ways you can help your search ranking, though. Look for similar terms, not exact — for example, if you were trying to rank for “ceiling fans” you might add “light fixtures” as another term.
You have to find the middle ground between too little and too much. That’s where your instincts as a writer and content marketer come in. Combine those with your knowledge of SEO to inform your content.
Alt Text
Alt text is the content that describes an image. If an image won’t load, the alt text tells the user what they are supposed to be seeing. You can read the alt text on images by hovering over them.
It also serves a couple of other important purposes.
- Accessibility: There are a number of regulations regarding accessible web browsing — alt text is central to those. Screen readers for visually impaired people rely heavily on alt text.
- Image SEO: Google’s algorithm is pretty good at recognizing what an image is about, but it’s very literal. Descriptive alt . You could post a picture of Santa Claus and Google might be able to tell that it’s Santa, but it won’t be able to tell that it’s actually Billy Bob Thornton in the movie Bad Santa — which changes the whole meaning of the image.

Most screen readers cut off at 125 characters, so make sure your alt text is short. You should make sure your description includes any keyword concepts that would help the page rank for search results. Alt text content doesn’t count against your keyword density for the text — but you should make sure to avoid keyword stuffing here too. Just a short, specific description is enough.
Hierarchy
The hierarchy of your site is incredibly important in today’s technical SEO. In one GoodFirms survey, bad navigation was one of the biggest reasons that people cited for leaving a website. And bad navigation doesn’t just hurt your website’s credibility with people. It hurts SEO too. Bad navigation doesn’t all fall on the content side — back end and mobile responsiveness matter a ton — but you can help.
Use HTML headings correctly. Think of them as titles for chapters, headings and subheadings. The H1 would be a chapter title, H2 is a heading and H3 and H4 should be used for subheadings. Heading tags are hierarchical, not linear. For example:

There should be a clear structure within your piece that runs from top to bottom. Use the correct heading structure. Your users will understand the flow of the content better and Google will award your content a better ranking.
Featured Snippet Content
If you’ve ever searched for an answer on Google and seen this, you’ve seen a featured snippet:
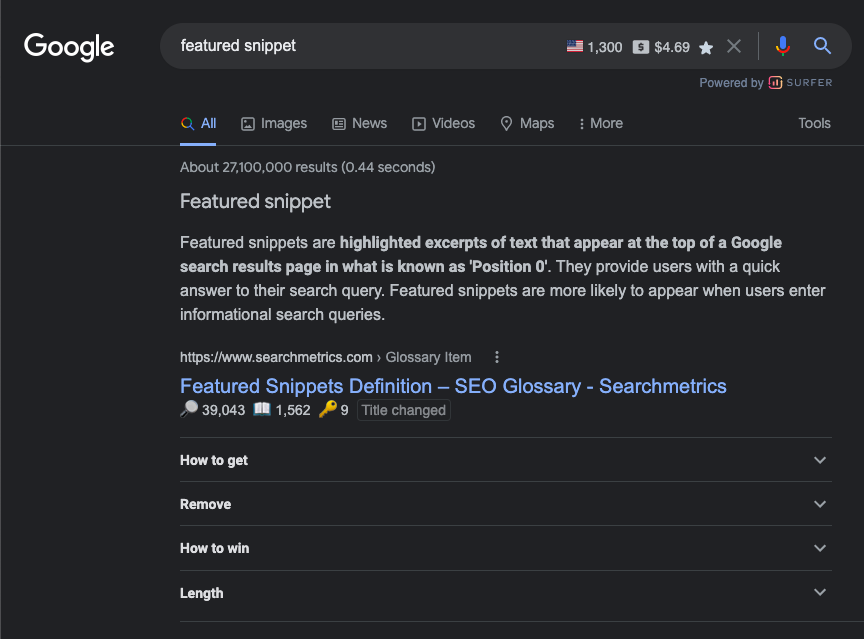
This is often called “Position 0” on the SERP. Some consider it as an even higher ranking result than the first search position..
To create featured snippet content, you need to understand what your audience is looking for. What questions are they asking? What are their pain points? Then use those insights to guide your research to create a concise answer that can be displayed as a featured snippet on a SERP.
Look for popular search terms without much competition. Find a way to answer the questions your audience has using those search terms. Once you have your keywords, wrap the question you’re trying to answer in an H2 header on the page — and then immediately provide the answer below the H2. Build the article with the Featured Snippet question and answer up front, then progress with your supplemental information from most to least important.
Search Engine Success
Use these best practices to build your ranking for the search terms that matter for your business, even if the low-hanging fruit is gone. And if you need a hand, contact us today — we’re here to help.
Best Regards,
David Brandon
Copywriter
Rainmaker Digital Services